Primary Joint Replacement
Primary Joint Replacement Surgeries are performed to repair severely damaged hips, knees and shoulders. This method is a definite process to remove pain in the joints, correct the deformities, restoring the mobility and improving the total overall functional status.
In primary joint replacement surgeries, the two most commonly done surgeries are: –
1. Total knee replacement surgery
2. Total hip replacement surgery
Other areas include shoulders, ankles, fingers and elbows.
KNEE REPLACEMENT
Introduction
Knee replacement or arthroplasty is a surgical process where the weight bearing surfaces of the knee joint are replaced by prosthesis. This process is done to decrease the pain and to reform the actions of the joints, wherein the ability to have free movements decreased.
There are many kinds of implants or prosthesis, which are used during the surgery.
The main materials used are: –
- Chromium alloys – Femoral component.
- cobalt alloys – Femoral component.
- Titanium alloys – Tibial component, Patellar Component.
- polyethylene – Tibial component
Other material’s used are Stainless steel uncemented implants, tantalum, and zirconium.
Zirconium is a new type of femoral implant, which is being used if there are any allergies seen.
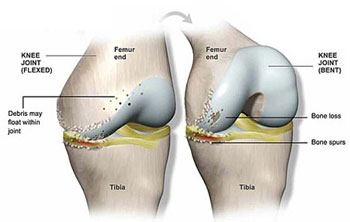
Causes: –
The main causes for total knee replacement are: -:
- Osteoarthritis
- Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Post Traumatic Arthritis.
Osteoarthritis (OA):-
It is a kind of joint disease, which is caused due to the breakdown of cartilage and the bone underneath. The most common symptoms are joint pain and stiffness. The symptoms generally show over the years. The main symptoms like joint pain and swelling, reduced mobility, generalised weakness of arms and legs are seen. Most commonly involved joints are the knee and hip joints.
Rheumatoid Arthritis: –
It is a chronic inflammatory disorder, which affects joints and other organs like skin, eyes, lungs, heart and blood vessels. In rheumatoid arthritis – the immune system of the body will affect other healthy tissues.
Post Traumatic Arthritis: –
This occurs due to any injury to any joint. It occurs due to wearing of the joint, which has any kind of injury. The injury could be due to accident due to vehicle injury, sports injury etc.
Procedure: –
Once the entire physical examination and a thorough knee examination are done – the procedure for the surgery begins. The procedure takes a minimum of 2 hours for completion. The anesthesia given are – general, epidural, nerve block.
The process is as follows: –
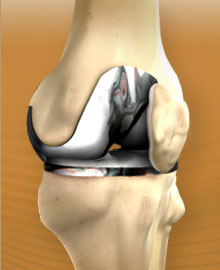
- The portion of the cartilage which is damaged, on tibia and femur are removed, along with some other portion of the bone.
- the removed portions of the cartilage and bone is then replaced by metal components – and can be cemented into the bone or even can be press-fit into the bone.
- the undersurface of patella is then cut and is resurfaced.
- a plastic spacer is then inserted in between the metal components, basically to create a gliding surface.
- the posterior cruciate ligament which stabilizes the knee joint is retained or a polyethylene post is substituted in place of it.
People can be subjected to partial knee replacement or total knee replacement. The patients who undergo TKR are usually in between 50 to 80 years.
Diagnosis: –
Diagnosis of the condition and thorough evaluation (pre – operative evaluation), should be done before advising to go for surgery. An extensive physical examination and medical history has to be taken, and should be seen that there are no side effects of any sort, in going forth to conduct the surgery.
The normal examination comprises of –
- To gain information about the patient’s health status and examination of the knee
- The knee must be examined in terms of stability, mobility strength and alignment
- X- Ray of the knee, MRI- knee is done
- Complete blood picture and ESR, RA factor are also done
- Renal function tests with uric acid
- Compete urinary examination and evaluation
Frequently asked questions: –
Knee Arthroplasty or TKR is surgical procedure, which is done to replace the weight bearing surfaces of the knee joint, so that pain and disability of the joints towards movements can be relieved.
The patient will experience some pain after surgery, and will decrease quickly by 4 to 5 days. Most people will be out of bed, and shall be walking by the day after surgery or the next by the help of walker.
Studies show that eighty five percent, who undergo TKR have functioning artificial joint.
Implants comprises of metal and medical grade plastic. The materials used to seal the components are: –
1) bone cement
2) a cement less approach which uses components, with porous coating which grows into tissues or can attach to bone.
Complications are usually low in General Anesthesia, epidural or regional nerve block.
RA and knee arthritis can develop at a young age.
There won’t be any link between food and development of infection. High protein intake helps towards fast wound healing.
Most medical insurances cover TKR – some cover it after 3 years of taking the policy.
Choosing an orthopedic surgeon is the most important part of the knee replacement process – Alongside the surgical team should have a well-endowed plan for post – operative rehabilitation.
People who have more advanced arthritis over both knees can consider a double knee replacement. However, there are certain risks and advantages associated with it.
Computer assisted surgery and custom cutting blocks are examples of newer technology. Minimally invasive knee replacement surgery is done to preserve muscle and soft tissues around knee, therefore helping to facilitate a faster and better recovery process.
Lifestyle modifications, medications, or alternative treatments like acupuncture and prolotherapy – which is injecting fluid to strengthen the connective tissue, will help in moderation for knee problems.
Mostly TKR procedures take 1.5 to 2 hours for completion. The orthopedic surgeon makes an incision, of 10 inches on the top of the knee and moves the kneecap – cuts the damaged bone and cartilage – which are then replaced with new metal and plastic components. These components combine together to form a synthetic joint, which function like that of the natural knee.
Complications include problems with wound healing, infection, DVT, and pulmonary embolism.
